
If you or someone close to you is managing a condition that requires blood thinners, you’ve probably heard of Warfarin. For decades, it's been the go-to prescription to prevent strokes and treat deep vein thrombosis (DVT). However, it’s not the easiest drug to manage—think frequent blood tests and dietary restrictions. Luckily, there's a bunch of alternatives out there, offering different benefits depending on your specific health needs.
Let's kick off with Edoxaban, a modern contender in the blood-thinning world. Known by its brand name, Lixiana, this alternative is a once-daily medication that inhibits Factor Xa, offering a smoother ride for those wary of extensive monitoring. Plus, its risk of causing gastrointestinal bleeding is on the lower side compared to some other options.
- Edoxaban (Lixiana)
- Dabigatran (Pradaxa)
- Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
- Apixaban (Eliquis)
- Aspirin
- Heparin
- Comparing Alternatives
Edoxaban (Lixiana)
So, what's the deal with Edoxaban, also known by its brand name Lixiana? In the landscape of Warfarin alternatives, Edoxaban stands out as a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) that conveniently inhibits Factor Xa, making it a solid choice for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation and the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE).
This modern blood thinner is all about ease. First things first, it’s a once-a-day tablet. That’s right, only one pill a day, which is pretty awesome if you’re not a fan of constantly remembering to take medication. Plus, you don't have to deal with the frequent blood monitoring that comes with Warfarin.
“Edoxaban offers a lower risk of major bleeding compared to Warfarin, especially when it comes to serious gastrointestinal bleeding,” says Dr. Helen Clark, a leading cardiologist.
For folks with moderate kidney function, this drug is a win. However, it's not recommended if your kidney function is severely impaired—in that case, steer clear of this option.
Pros
- Once-daily dosing makes it convenient.
- Lower risk of gastrointestinal bleeding than some other DOACs.
- Effective in staving off strokes and preventing thrombosis.
Cons
- No specific antidote if you need to reverse the effects quickly.
- Not suitable for those with severe kidney issues.
- Less long-term data available compared to some other blood thinners.
While Edoxaban is relatively new on the scene compared to some, it's certainly making waves as a viable alternative to traditional blood thinners. It's all about balancing convenience with effectiveness and safety. Considering all this, Edoxaban could be a worthwhile option if you're after a modern solution with fewer hassles.
Dabigatran (Pradaxa)
Dabigatran, sold under the brand name Pradaxa, is one of the first among the newer oral anticoagulants that provide an alternative to the traditional Warfarin. Unlike Warfarin, Dabigatran doesn’t require frequent blood monitoring, which is a huge relief for many folks.
Pradaxa specifically targets thrombin, an important player in blood clot formation. This is especially useful for those managing atrial fibrillation that's not related to a heart valve issue. It's like having a targeted strike team rather than a broad-spectrum approach.
Here are some of the major pros and cons if you're considering Dabigatran:
Pros
- No routine blood monitoring needed, simplifying life for you and your healthcare team.
- Reversal agent available called idarucizumab (Praxbind), which is a peace of mind if bleeding complications arise.
- Quick onset of action means it starts working faster than Warfarin.
Cons
- Twice-daily dosing might be a bit of a hassle if you’re juggling a lot of medications.
- Potential for gastrointestinal side effects, such as an upset stomach.
- Can be pricey without insurance or coverage plans.
If you've got moderately impaired kidney function, timing the doses might be crucial, as its clearance is partly renal. Planning to munch on a feast? No problem with Pradaxa, as food doesn’t significantly affect its absorption. But remember, always talk to your doctor to determine if it fits well with your medical history and lifestyle.
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
Here's one you might have come across—Rivaroxaban, better known by its brand name, Xarelto. This alternative to Warfarin is another heavy hitter when it comes to managing blood clots. Whether you're dealing with atrial fibrillation or looking to prevent DVT after surgery, Xarelto steps up with a little less hassle than the old standard.
One of the coolest things about Rivaroxaban is that it doesn’t require the strict dietary restrictions or frequent blood tests that Warfarin demands. Thank goodness you can enjoy your leafy greens without stressing about vitamin K! Plus, it’s usually taken once a day, which is great for those of us who find it tricky to remember multiple doses.
Pros
- Convenient once-daily dosing makes life a bit simpler.
- No routine blood monitoring needed—hooray for fewer needle pokes!
- Effective in preventing stroke in atrial fibrillation.
- Lower risk of some types of bleeding compared to Warfarin.
Cons
- No specific reversal agent exists, which might be a concern during emergencies.
- Cost might be a factor—it's often pricier than generic medications like Warfarin.
- It may not be suitable for patients with significant kidney or liver issues.
For those curious about the numbers, a few studies have shown Xarelto holding its ground well against Warfarin in preventing strokes. A big plus for many is that it simplifies the process without losing effectiveness. Just like any medication, it isn't a one-size-fits-all solution, so chat with your healthcare provider to see if it's a good fit for you.
Apixaban (Eliquis)
When it comes to blood thinners, Apixaban, commonly known by its brand name Eliquis, is making waves among those looking for alternatives to Warfarin. Apixaban is particularly appealing because of its strong record in preventing strokes and systemic embolism in folks with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (AF).
One thing that makes Eliquis a standout is its safety profile. Sure, all anticoagulants carry some bleeding risk, but Apixaban has a good track record here. Studies have shown that it tends to cause less bleeding compared to some other options, especially in patients with kidney troubles.
But remember, it’s not a one-size-fits-all. Apixaban is typically taken twice a day, which might be a bummer for some folks who prefer once-daily dosing. Yet, on the bright side, it doesn't require the same regular blood monitoring that Warfarin demands, which can feel like a big relief.
Pros
- Lower bleeding risk compared to some other anticoagulants.
- No need for routine blood test monitoring.
- Favorable for patients with renal impairment.
Cons
- Twice-daily dosing schedule, which can affect adherence for some.
- Cost may be higher without insurance coverage.
For anyone considering switching from Warfarin to another anticoagulant, it’s essential to discuss the options with your healthcare provider. Each choice comes with its own set of pros and cons, and Apixaban is no different. It shines in many areas but knowing your personal health situation will guide whether it’s the right fit.
| Apixaban Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Dosing Frequency | Twice Daily |
| Routine Monitoring | Not Required |
| Bleeding Risk | Lower |
Aspirin
When you think of Aspirin, you might picture a simple pill for headaches or preventing heart attacks. What you might not know is that it also doubles up as a blood thinner. For decades, doctors have been recommending low-dose Aspirin for people at risk of heart attacks and strokes due to its ability to inhibit platelet aggregation. In simpler terms, it stops the blood cells from sticking together and forming clots.
Now, here's the thing: while Aspirin can be a good option for some, it's not perfect. It doesn’t require lifestyle changes or regular blood tests like Warfarin, which is a big plus. But it does have a downside – stomach irritation. Yup, taking it regularly can mess with your tummy and even cause bleeding ulcers for some folks.
Pros
- Affordable and widely available.
- No need for frequent blood level monitoring.
- Easy to incorporate into daily routine without major dietary restrictions.
Cons
- Can cause stomach irritation and increase bleeding risk in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Not effective enough for all patients at risk of clots.
- Some people can develop a resistance over time.
So, while Aspirin is a handy option, it’s often just right for those with mild risk or when combined with other treatments. Always chat with your doctor to see if it’s the right fit for your situation.
Heparin
Heparin is one of those tried-and-true options that’s been around the block a few times. It's a natural substance, mainly used in hospitals due to its fast-action capability. If you’re in need of immediate action—let’s say after surgery or if you’re at a high risk for a clot—it’s very effective.
So, how does Heparin work? It acts by directly disrupting the clotting process, which makes it incredibly reliable for short-term, high-stakes situations. You can get it either through an injection or an IV, which means it starts working almost instantly.
Another cool fact is that Heparin comes in two main forms: Unfractionated Heparin and Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH). LMWH is a bit easier to manage, requiring less monitoring, and it’s often used for folks heading home but still needing some anticoagulation coverage.
Pros
- Rapid onset of action makes it ideal for emergency situations.
- Flexibility in administration (injection or IV).
- Unfractionated form can be easily monitored and adjusted.
- Has a known reversal agent, Protamine sulfate, for minimizing bleeding risks.
Cons
- Can’t be taken orally, so not the most convenient option for long-term use.
- Requires regular monitoring, especially for unfractionated Heparin.
- Can cause heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), a serious condition that reduces platelets.
Although Heparin is up for the task of handling those emergency situations, it’s not something you’d want to rely on outside a hospital setting for extended durations. But, when you need quick, effective anticoagulation, it’s tough to beat.

Comparing Alternatives
When you're tasked with juggling options for managing your blood's tendency to clot, it can feel like you're choosing from a surprisingly varied menu. From traditional warhorses like Warfarin to newer contestants like Edoxaban, each has its quirks. So, let's break it down to see how these options stack up and what might work best for you or your loved ones.
The newer Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs) like Edoxaban, Rivaroxaban, Dabigatran, and Apixaban have changed the game with their convenience. Imagine the freedom of not having to go in for regular blood tests! Plus, these drugs come with fewer dietary restrictions, and for many, that’s a big win. Each has its edge, though—they differ slightly in how they work, their dosing schedules, and potential reversal agents.
Take Edoxaban, for example. It offers the simplicity of once-a-day dosing and boasts a lower risk of causing severe bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract compared to some of its peers. But, on the downside, there’s no specific reversal agent if things go sideways, and it’s not the best choice if someone has severe kidney issues.
| Medication | Dosing | Reversal Agent | Bleeding Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warfarin | Variable | Yes - Vitamin K | Moderate-High |
| Edoxaban (Lixiana) | Once Daily | No specific agent | Lower gastrointestinal risk |
| Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) | Once Daily | Yes - Andexanet alfa | Moderate |
| Apixaban (Eliquis) | Twice Daily | Yes - Andexanet alfa | Lower overall |
| Dabigatran (Pradaxa) | Twice Daily | Yes - Idarucizumab | Moderate |
The appeal of DOACs is clear, but there’s also the ever-familiar Aspirin and Heparin. Aspirin, though not as potent as the rest, can be sufficient for low-risk cases. Meanwhile, Heparin is an injectable option primarily used in hospitals, which has its place but isn't as practical for long-term management at home.
At the end of the day, there's no one-size-fits-all solution. It's about matching the right medication to your unique needs and conditions. Have a chat with your healthcare provider, lay out the options, and consider the lifestyle and health factors that matter most. Armed with the right info, you can make an informed choice that fits squarely into your life.
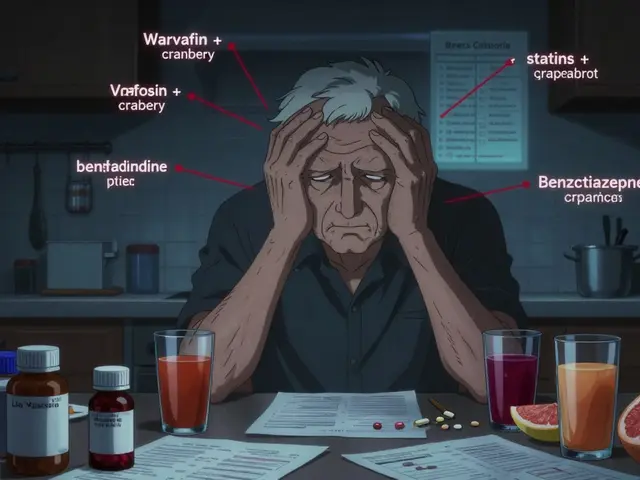



Jay Ram
April 2, 2025 AT 00:20I've been on a blood thinner for a few years and the move to a DOAC really cut down my clinic visits.
Skipping the monthly INR checks felt like getting my life back.
The once‑daily pills are easy to fit into a busy schedule.
Just remember to keep an eye on kidney function, especially with the newer agents.
If your doc thinks it's right for you, the hassle factor alone is worth a look.
Elizabeth Nicole
April 13, 2025 AT 14:07The landscape of anticoagulation has transformed dramatically over the past decade.
Where once warfarin ruled the roost, a suite of direct oral anticoagulants now offers patients real flexibility.
Edoxaban stands out for its once‑daily dosing and a comparatively lower gastrointestinal bleeding profile.
Rivaroxaban shares that convenience, but its lack of a universally available reversal agent still raises eyebrows in some circles.
Dabigatran introduced the first specific antidote, idarucizumab, giving clinicians a safety net that was previously missing.
Apixaban, despite its twice‑daily schedule, consistently demonstrates a lower overall bleed risk in large trials.
Aspirin, while inexpensive, simply isn’t potent enough for most high‑risk atrial‑fibrillation patients.
Heparin remains the go‑to in hospitals for immediate anticoagulation, but its requirement for injections limits long‑term use at home.
When you factor in kidney function, the choice narrows further, because drugs like dabigatran and edoxaban need dose adjustments or avoidance.
Cost is another practical hurdle; many insurers cover the newer agents, yet out‑of‑pocket expenses can still surprise patients.
Lifestyle considerations, such as dietary restrictions, become almost irrelevant with most DOACs, freeing patients from the vitamin K calculus.
The availability of reversal agents for rivaroxaban and apixaban (andexanet alfa) adds a layer of confidence during emergency surgeries.
As clinicians, we strive to match the medication not just to the disease but to the person's daily rhythm and preferences.
Patients who value simplicity often gravitate toward once‑daily options like edoxaban or rivaroxaban, while those willing to manage twice‑daily dosing may benefit from apixaban’s safer bleed profile.
Ultimately, an open conversation with your healthcare team, armed with these nuances, empowers you to make an informed, personalized decision.
Dany Devos
April 25, 2025 AT 03:53From a clinical efficacy standpoint, the evidence base for apixaban remains superior to warfarin in most atrial fibrillation cohorts.
Sam Matache
May 6, 2025 AT 17:40Honestly, the hype around these shiny new pills can feel like a circus, but they do deliver on the promise of fewer lab trips.
People love bragging about taking a pill once a day and never having to cook special meals.
Meanwhile, the pharmaceutical giants are cashing in, and the price tags reflect that.
If you’re not prepared to swallow the cost, warfarin still does the job, albeit with more paperwork.
Hardy D6000
May 18, 2025 AT 07:27While you romanticize the “cost” narrative, the reality is that many American patients lack affordable options, making the “once‑daily” convenience a luxury rather than a universal benefit.
Our healthcare system should prioritize accessibility over flashy dosing schedules.
Amelia Liani
May 29, 2025 AT 21:13It’s heartening to see such a thorough breakdown; patients often feel overwhelmed by the sheer number of choices.
Remember that the emotional burden of daily monitoring can be just as taxing as the medication side effects.
Finding a balance between clinical efficacy and personal comfort is key, and sharing stories like yours helps demystify the process for everyone.
shikha chandel
June 10, 2025 AT 11:00The epistemic hierarchy of anticoagulants clearly places DOACs above traditional agents, albeit with nuanced pharmacodynamic considerations.
Zach Westfall
June 22, 2025 AT 00:47Whoa this takes the conversation to another level the nuance of cost is real and we cant ignore the disparity everyone deserves a fair shot at the best meds even if it means lobbying for better insurance coverage
Pranesh Kuppusamy
July 3, 2025 AT 14:33In the grand tapestry of therapeutic decisions, anticoagulation epitomizes the intersection of empirical evidence and individual destiny; the physician’s role is to illuminate pathways while honoring the patient’s agency.
Thus, every prescription should be a dialogue rather than a decree.
Crystal McLellan
July 15, 2025 AT 04:20yeah sure the “tape” says everything is safe but you never hear about the hidden risks the big pharma pull the strings and the studies are rigged dont trust the mainstream narrative