
When a loved one is starting capecitabine, the flood of medical jargon can feel overwhelming. This guide cuts through the noise, giving patients and caregivers clear answers about what the drug does, how it’s taken, what to expect, and how to manage everyday challenges.
What is Capecitabine?
Capecitabine is an oral chemotherapy agent that the body converts into the active chemotherapy fluorouracil (5‑FU). It was approved by the FDA in 1998 for metastatic colorectal cancer and later for certain breast cancers. Because it’s taken as a pill, it lets patients avoid frequent IV visits, but it still carries the same potency as traditional 5‑FU.
How Does Capecitabine Work?
The drug travels through the bloodstream and is activated primarily inside tumor cells. Enzymes in the cancerous tissue convert capecitabine into 5‑FU, which then interferes with DNA synthesis, halting cell division. This tumor‑selective activation helps spare healthy tissue, though side effects still arise because some normal cells also process the drug.
When Is Capecitabine Prescribed?
- Colorectal cancer - metastatic or adjuvant settings after surgery.
- Breast cancer - especially HER2‑negative tumors in combination with other agents.
- Gastric and pancreatic cancers in specific clinical trials.
Oncologists may also use capecitabine as a maintenance therapy after the initial intensive treatment phase.
Typical Dosage and Scheduling
Capecitabine is usually prescribed in two‑week cycles: 14 days of pills followed by a 7‑day break. The exact dose depends on body surface area (BSA), kidney function, and the cancer type.
- Calculate BSA (most clinics use the Mosteller formula).
- Typical adult dose for colorectal cancer: 1250 mg/m² twice daily.
- For breast cancer: 1000 mg/m² twice daily.
- Take each dose within 30 minutes after a meal to reduce stomach upset.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember unless it’s less than 8 hours before the next scheduled dose - then skip it.
Kidney impairment requires dose reductions; your oncologist will adjust accordingly.
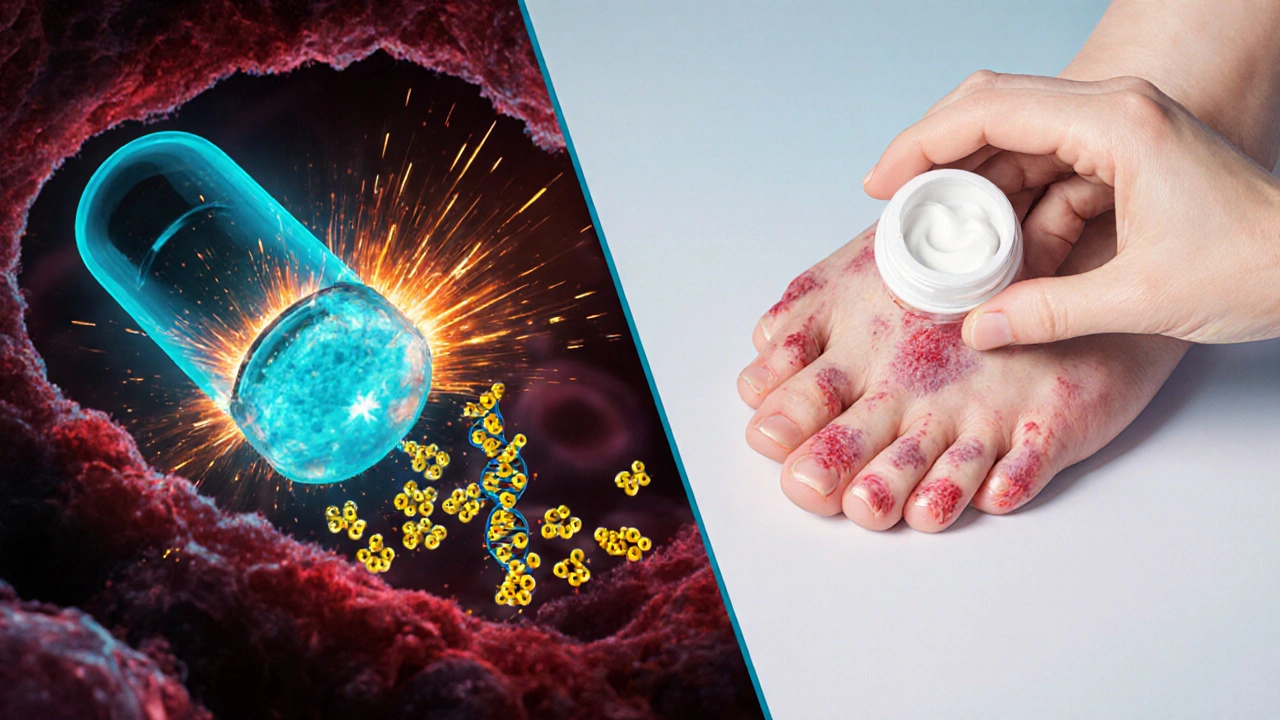
Common Side Effects and How to Manage Them
Even though capecitabine is taken at home, side effects can feel intense. Knowing what to expect makes it easier to act quickly.
- Hand‑foot syndrome - redness, swelling, or peeling on the palms and soles. Keep skin moisturized, avoid tight shoes, and report severe pain to your doctor.
- Nausea and vomiting - take anti‑emetics before meals, eat small frequent meals, and stay hydrated.
- Diarrhea - use loperamide as directed, and monitor stool consistency. Severe diarrhea can lead to dehydration, so contact your care team promptly.
- Fatigue - prioritize rest, light exercise, and a balanced diet rich in protein.
Blood tests are usually done before each cycle to check blood counts and liver/kidney function. Low white blood cells (neutropenia) may require a temporary pause.
Drug Interactions and Precautions
Capecitabine can interact with several common medications. Always share a complete medication list with your oncology team.
- DPYD gene deficiency - a rare genetic variant that reduces the ability to break down 5‑FU, leading to severe toxicity. Some clinics test for DPYD before starting treatment.
- Anticoagulants (warfarin, direct oral anticoagulants) - increased bleeding risk.
- Fluoropyrimidine‑based regimens - avoid overlapping with other 5‑FU drugs.
- Herbal supplements (St. John’s wort, ginseng) - may alter drug metabolism.
If you’re taking over‑the‑counter pain relievers, stick to acetaminophen unless your doctor advises otherwise.
Comparing Capecitabine to Intravenous 5‑FU
| Aspect | Capecitabine (oral) | 5‑FU (IV) |
|---|---|---|
| Administration | Twice‑daily pills | Infusion over 10‑30 min or continuous 24‑hr pump |
| Convenience | Home‑based, no IV line | Clinic visits required |
| Common side effects | Hand‑foot syndrome, diarrhea, nausea | Mucositis, neutropenia, cardiac toxicity (rare) |
| Typical dose schedule | 2 weeks on, 1 week off | Weekly or bi‑weekly infusions |
| Cost (US, 2025) | ~$4,800 per 2‑week cycle | ~$5,200 per cycle (including infusion fees) |
Both regimens deliver the same active molecule, but the oral route often feels less intrusive. However, adherence becomes a personal responsibility - missing doses can reduce effectiveness.

Tips for Caregivers
- Set up a medication calendar. Use phone alarms or a pill organizer labeled with cycle days.
- Track side effects daily in a simple journal. Note severity, timing, and any actions taken.
- Stay on top of lab appointments. Bring a list of recent test results to each oncology visit.
- Prepare skin‑friendly care kits: fragrance‑free moisturizers, soft socks, and cool compresses for hand‑foot syndrome.
- Encourage hydration - aim for at least 2 L of fluid each day unless fluid restriction is ordered.
Emotional support matters, too. Simple gestures like a favorite meal or a short walk can boost morale during the tough weeks.
When to Call the Doctor
Knowing the red‑flag signs can prevent emergencies.
- Fever above 100.4 °F (38 °C) with chills - possible infection due to low neutrophils.
- Severe or worsening hand‑foot pain that interferes with walking.
- Persistent vomiting that prevents keeping fluids down.
- New or worsening shortness of breath - rare cardiac toxicity.
- Unexplained bruising or bleeding.
In any of these cases, contact the oncology nurse line or go to the nearest emergency department.
Quick Takeaways
- Capecitabine is an oral pro‑drug that becomes 5‑FU inside tumor cells.
- Typical schedule: 14 days on, 7 days off; dose based on body surface area.
- Most common side effects: hand‑foot syndrome, nausea, diarrhea, fatigue.
- Check for DPYD gene variants before starting - it can prevent severe toxicity.
- Caregivers play a crucial role in medication adherence, side‑effect monitoring, and emotional support.
Can I take capecitabine with food?
Yes. Take each dose within 30 minutes after a meal. Food helps reduce stomach irritation and improves absorption.
What should I do if I develop hand‑foot syndrome?
Stop applying harsh creams, keep the skin moisturized with fragrance‑free lotion, wear loose‑fitting shoes, and inform your oncologist. Dose reduction or a short break may be recommended.
Is genetic testing for DPYD required?
Many cancer centers now test for DPYD variants before starting capecitabine because a deficiency can cause dangerous toxicity. Ask your oncologist if testing is part of the protocol.
Can I drink alcohol while on capecitabine?
Moderate alcohol is usually okay, but heavy drinking can worsen liver toxicity and increase nausea. Discuss your drinking habits with the care team.
How often will I need blood tests?
Typically before each new cycle (every 3 weeks) to check blood counts, liver enzymes, and kidney function. More frequent testing may be ordered if side effects appear.



Shannon Stoneburgh
October 24, 2025 AT 20:15Capecitabine sounds like another overhyped pill. Most patients just end up dealing with nasty side effects.
Nathan Comstock
October 26, 2025 AT 00:02Listen, the real problem is that we’re letting pharma push toxic drugs without proper scrutiny! America deserves better than endless chemo cycles!
Corrine Johnson
October 27, 2025 AT 02:49One must consider the philosophical underpinnings of oral chemotherapies, - they promise autonomy yet deliver burden; the paradox is palpable, indeed, the patient is granted freedom to swallow a pill, but simultaneously shackled by relentless monitoring, thus the illusion of control becomes a masquerade, doesn’t it?
Jennifer Stubbs
October 28, 2025 AT 06:35The data clearly shows that adherence drops when patients feel isolated; hand‑foot syndrome alone leads to dose reductions in up to 30 % of cases, and the consistent blood work is a logistical nightmare for many, so a pragmatic approach to scheduling and supportive care is essential.
Abby W
October 29, 2025 AT 10:22💡Just a heads‑up: setting multiple alarms on your phone can actually save you from missing a dose, and don’t forget to keep a waterproof band‑aid kit handy for any skin irritation! 🙏
Veronica Appleton
October 30, 2025 AT 14:09Make a simple calendar and mark the on/off days, track side effects in a notebook and bring it to every appointment, stay hydrated and use fragrance‑free lotion for hand‑foot issues, these steps really help.
the sagar
October 31, 2025 AT 17:55They’re hiding the real cure, just don’t trust the pharma.
Charlie Stillwell
November 1, 2025 AT 21:42Honestly the whole capecitabine regimen is just a cost‑effective façade for intravenous 5‑FU, the pharmacokinetics are identical and the side‑effect profile remains brutal, plus the insurance paperwork is a nightmare, so why bother with oral administration?
Ken Dany Poquiz Bocanegra
November 3, 2025 AT 01:29While the oral route is convenient, the key is diligent monitoring; keep a log, stay in touch with your nurse, and don’t ignore early signs of toxicity.
Tamara Tioran-Harrison
November 4, 2025 AT 05:15The notion that an oral tablet can magically replace the clinical rigor of an IV infusion is, at best, a marketing spin.
The capecitabine, after all, is merely a pro‑drug that must be metabolized into 5‑FU, and that metabolic step is fraught with variability.
Patients with compromised renal function often experience exaggerated toxicity, a fact that is glossed over in glossy brochures.
The hand‑foot syndrome, though frequently described in mild terms, can progress to ulceration, forcing dose reductions or even treatment cessation.
Moreover, the requirement for bi‑weekly blood work defeats the convenience narrative, as many patients must travel to distant labs.
Insurance companies, eager to cut costs, sometimes approve the oral version without ensuring proper DPYD testing, exposing patients to unnecessary risk.
The literature demonstrates that adherence rates hover around 70 %, meaning nearly a third of patients are not receiving the intended therapeutic exposure.
From a pharmacoeconomic perspective, the pill may appear cheaper, but the downstream costs of managing side effects often outweigh any initial savings.
Physicians who champion capecitabine must therefore bear the responsibility of close monitoring, patient education, and rapid intervention.
It is not enough to simply hand a prescription and say ‘take it with food’; a comprehensive support plan is indispensable.
The emotional toll on caregivers is also significant, as they must become de facto pharmacists, tracking doses and side‑effects.
In reality, the oral route transforms part of the treatment burden from the clinic to the home, which is not inherently better.
Thus, the claim of superiority is situational and hinges on the individual’s capacity for self‑management.
Patients should be encouraged to discuss their lifestyle, comorbidities, and support system before committing to capecitabine.
Only then can the decision be truly patient‑centered rather than driven by pharmaceutical convenience.
kevin burton
November 5, 2025 AT 09:02Following these points, a structured diary and regular check‑ins with the oncology nurse can mitigate many of the risks associated with capecitabine therapy.
Buddy Bryan
November 6, 2025 AT 12:49Even though the advice sounds basic, implementing it aggressively can cut down emergency visits and improve overall outcomes.
Terell Moore
November 7, 2025 AT 16:35Ah, the ever‑glamorous world of oral chemotherapies, where the illusion of convenience masks a cascade of bureaucratic and physiological absurdities-truly a testament to modern medicine's love affair with complexity.
Amber Lintner
November 8, 2025 AT 20:22Obviously the whole system is rigged to keep us guessing, but hey, at least we get to choose between pills and needles, right?
Lennox Anoff
November 10, 2025 AT 00:09I suppose one could argue that the variability in patient experiences validates a flexible approach, yet the data stubbornly points to consistent challenges across demographics; therefore, personal preference should never override clinical prudence.